Unlocking Bioenergy Wealth: A Guide to 1 TPH Palm EFB Pellet Line Investment in Indonesia
Indonesia, the world’s largest palm oil producer, is currently sitting on a massive, yet often underutilized, resource: Empty Fruit Bunches (EFB). This lignocellulosic biomass waste, traditionally challenging to manage, is now commanding high prices as premium bio-fuel in the international energy market.
For international investors and enterprises, deploying a 1 Ton Per Hour (1 TPH) Palm EFB Pellet Production Line in Indonesia represents a strategic entry point into the lucrative biomass export sector. Henan Xuezhao Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd. specializes in engineering robust, high-efficiency pelletizing solutions designed to master the unique properties of EFB.

Biomass energy production line
1. The Undeniable Business Case for EFB Pellets in Indonesia
The Indonesian market provides a powerful trifecta for EFB pellet manufacturing:
- Vast, Low-Cost Feedstock: EFB is generated in continuous, enormous volumes at Palm Oil Mills (POMs). This guarantees a stable, year-round supply of raw material at minimal cost, drastically improving profit margins compared to wood pellets.
- Government Mandate: Indonesia’s commitment to renewable energy, including mandatory biomass co-firing in coal power plants, ensures a robust domestic absorption capacity for the product.
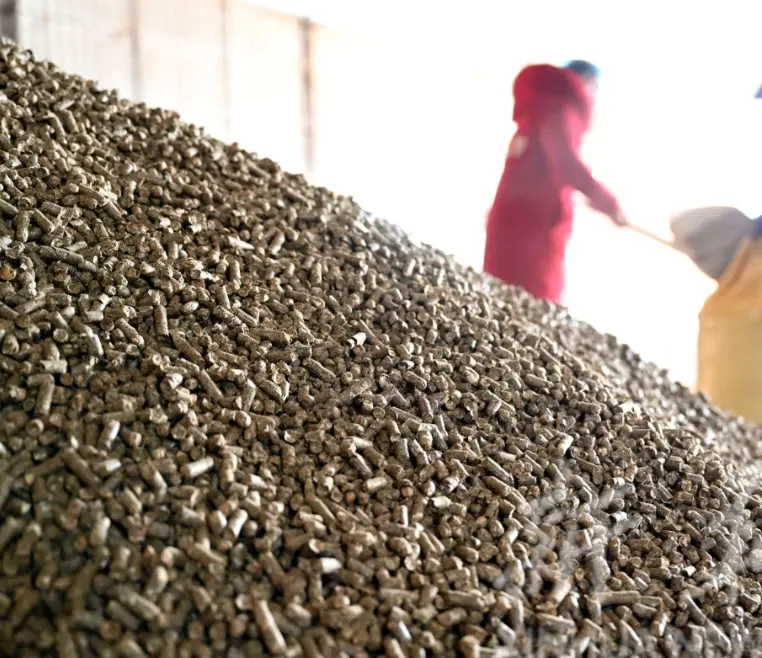
- Export Premium: High-quality EFB pellets(Calorific Value > 4000 kcal/kg) are a highly desirable product for power generation in Japan and Korea, fetching superior prices and driving exponential ROI.

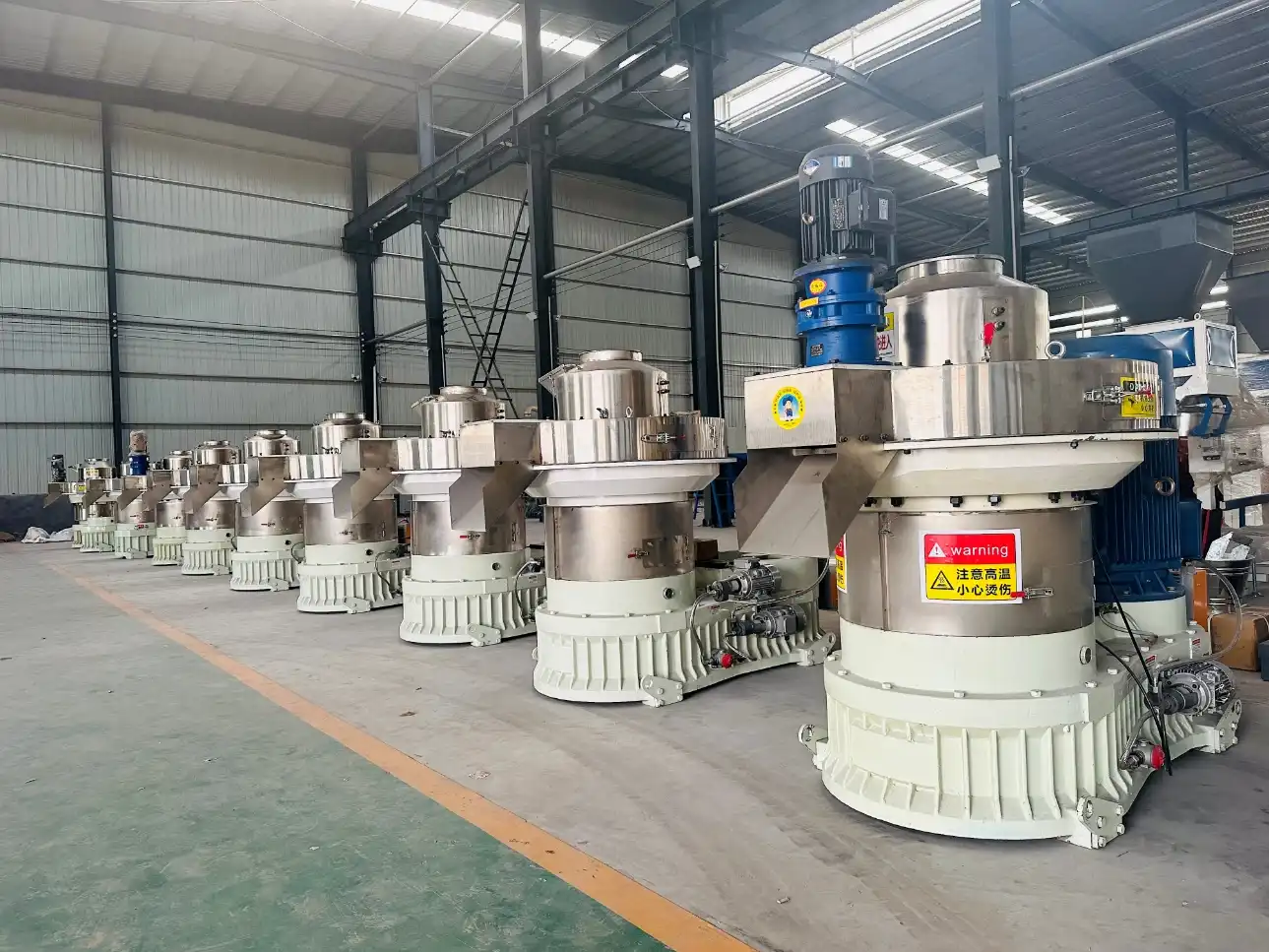
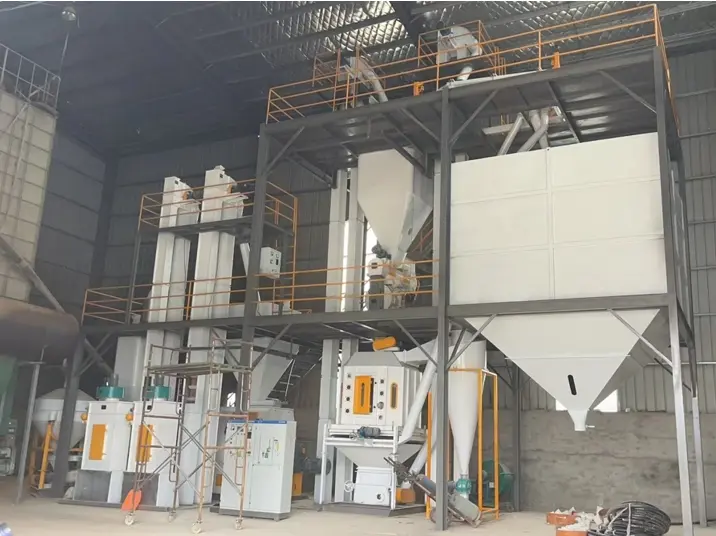
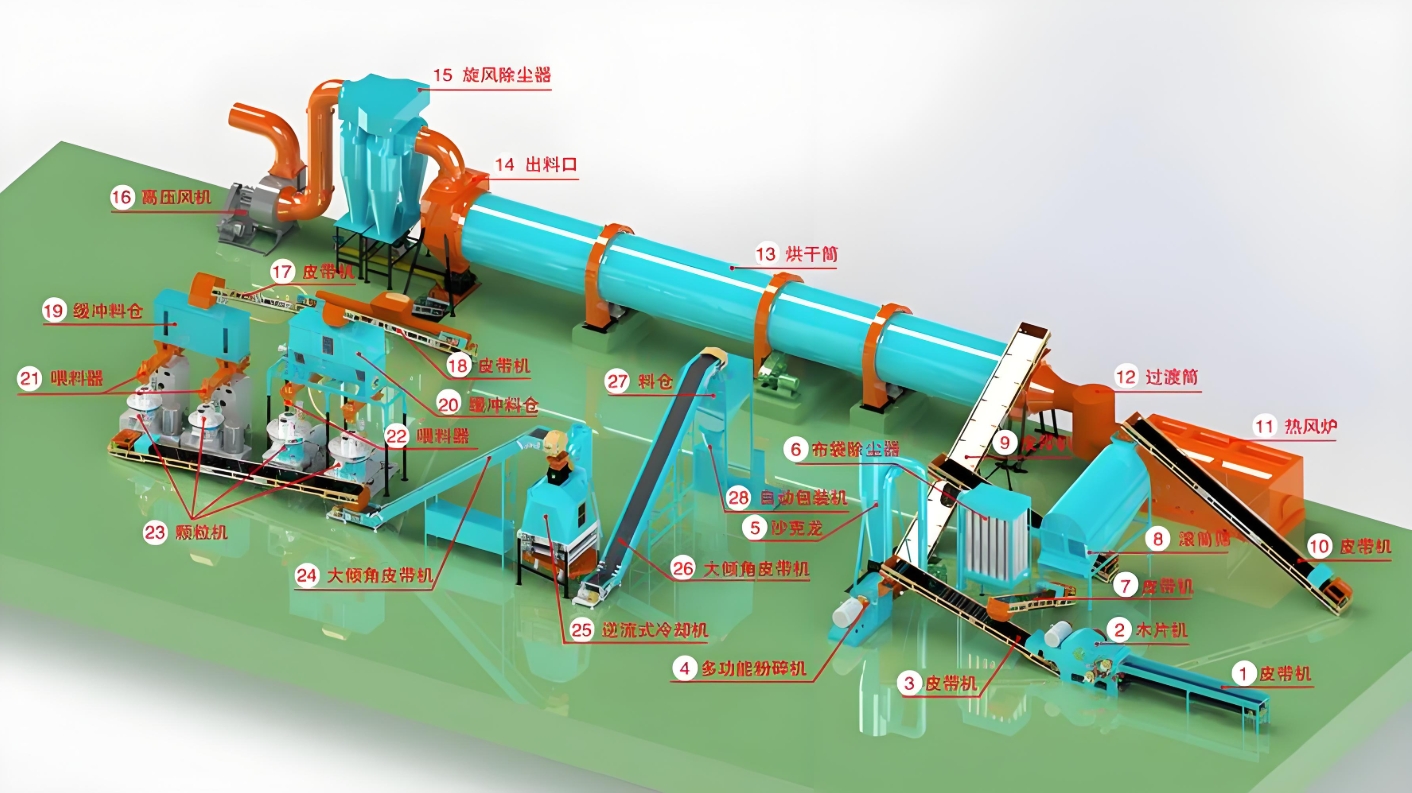
2. Mastering the Technology: 1 TPH EFB Pellet Line Configuration
EFB presents technical challenges due to its long, tough fibers and high moisture content (up to 60%). A successful 1 TPH line must integrate specialized machinery to handle this material efficiently. Here is the essential equipment layout provided by Henan Xuezhao Machinery:
| Production Phase | Core Equipment (Xuezhao Solution) | Technical Necessity |
| Fiber Preparation | Heavy-Duty EFB Shredder / Chipper | Required to cut the tough, stringy EFB fibers into manageable lengths (15−50mm) for subsequent processing. |
| Drying | Three-Pass Rotary Dryer | Crucial for EFB. The moisture content must be precisely reduced to the optimal 10-15% range. This is the most energy-intensive step. |
| Grinding | High-Efficiency Hammer Mill | Pulverizes the dried, shortened fibers into fine powder (<8mm), preparing the material for compression. |
| Pelletizing | Ring Die Pellet Mill (with Force Feeder System) | The heart of the line. A force feeder is non-negotiable for EFB, as it ensures consistent material delivery into the high-pressure ring die chamber, overcoming EFB’s low bulk density. |
| Post-Processing | Counter-Flow Cooler & Packaging System | Cools and hardens the fresh pellets, increasing durability for long-distance export shipping, followed by automated weighing and bagging. |
3. Strategic Considerations for Maximum Profitability
To maximize the return on investment (ROI) for an EFB Pellet Line Indonesia project, investors must focus on three key operational areas:
- Proximity to Source: Locating the plant close to a cluster of Palm Oil Mills drastically reduces the logistical cost of raw material transportation, which can be the largest operational expense.
- Energy Consumption Management: Due to the high-moisture content, the dryer is the primary energy sink. Choosing an advanced, thermally efficient drying solution is paramount to lowering the cost per ton.
- Durable Component Selection: EFB processing is abrasive. Investing in high-quality, specialized ring dies and rollers from a reliable supplier like Henan Xuezhao Machinery minimizes downtime and maintenance costs.
Conclusion: The investment in a 1 TPH EFB Pellet Line in Indonesia is more than an environmental solution; it is a direct path to accessing the high-value global biomass fuel trade. With the right technology and strategic planning provided by Henan Xuezhao Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd., the vast EFB resources of Indonesia can be efficiently monetized, delivering significant and sustainable returns.

Q&A (Questions and Answers)
Q1: What makes the Ring Die Pellet Mill suitable for EFB compared to Flat Die designs?
A1: The Ring Die design is preferred for large-scale EFB production because it provides a higher level of continuous pressure, better heat distribution, and is more robust for tough fibers. Crucially, it accommodates the necessary force feeder system required to densify low-density EFB material effectively.
Q2: What is the main risk associated with EFB pellet production in Indonesia?
A2: The primary risk is often related to material consistency and moisture management. Inconsistent EFB quality from various suppliers, coupled with potential high rainfall in Indonesia, requires robust pre-treatment and a highly reliable drying system to maintain the 10−15% moisture standard for quality pellets.
Q3: Does Henan Xuezhao Machinery provide full setup support for Indonesian clients?
A3: Yes, Henan Xuezhao Machinery offers a complete turnkey service, including customized plant layout based on local site conditions, manufacturing and supply of the entire EFB pellet line, on-site installation supervision and commissioning, technical training, and guaranteed long-term supply of high-wear parts like dies and rollers.





